Ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy
Metallurgical applications accounted for about 19% of global demand in 2010, this is due to the fact that rare earth elements increase the quality of stainless and high-speed steels, siliceous and heat-resistant steels, cast iron, since REE are deoxidizers and desulfurizers. They are introduced into steel in the form of a mishmetal. An alloy of iron with a large number of metals of the cerium group makes it possible to create materials with pyrophoric properties that are used in tracer bullets, shells, flints for lighters.
REE is also alloyed with cast iron, so cast iron doped with yttrium has high mechanical and casting properties, which allows it to be used for the production of critical parts of internal combustion engines. In non-ferrous metallurgy, these are light alloys for aviation and space technology Al-Mg and Mg-Zr (REE additives in them from hundredths of a percent to 3-5%), the introduction of REE into these alloys increases their strength, ductility and resistance to oxidation when heated.
For alloying, mishmetall is usually used, but the best results are achieved with the use of neodymium. In addition, non-ferrous metal alloys with REE are used in nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. NiMH batteries have shown the highest growth rates in this sector over the past decade, which was initially driven by an increase in demand for portable electronic equipment, and then the use of these batteries in hybrid vehicle (HEV) power systems.
Glass and ceramic industry
This industry is a fairly large consumer of rare earth metals for the production of special glasses of photooptics and lighting equipment. Individual REE oxides are used for discoloration and coloring of glasses, giving them the ability to absorb and transmit various radiations (IR, UV, X-rays, etc.), to increase their heat resistance. The industry consumes REE oxides (Ln2O3= La, Ce, Nd, Eu purity of oxides 98.5- 99%).
So glass with the addition of 2-4% cerium oxide is used for protective glasses during glass blowing and welding works, as they do not transmit UV radiation. In addition, this glass does not tarnish under the influence of radioactive radiation, which allows it to be used for boxes in nuclear technology.In the ceramic industry, REE oxides are used to color porcelain, glazes, enamels and give them opacity.
In addition, yttrium oxide is used to produce stabilized ceramics based on zirconium dioxide that can withstand temperatures up to 2200 °C, which can be used as a material for thermal barrier coating.Lanthanum and yttrium chromites stabilized by SCHZE are used for the manufacture of refractory ceramics, from which the heating elements of electric furnaces operating in an oxidizing atmosphere at temperatures of 1600-1900 °C. are produced.
Production of polishing materials
Polishing materials based on REE oxides provide high quality of the polished surface with lower material consumption and higher speed compared to other materials (zinc oxides, zirconium, aluminum, etc.). Cerium oxide Ce2O3 (polyrite) is mainly used as polishing powders for the manufacture of optical glasses and semiconductor materials.
Chemical, light and petrochemical industry
Manufacture of lacquers, paints, light compounds, ammonia synthesis catalysts, photo equipment and autocatalysts.
Salts of light rare earth metals and cerium are used in the production of catalysts for catalytic cracking FCC (cracking in a fluidized bed using a fluidized catalyst).
Cerium oxide is the main component of catalysts for afterburning toxic components of exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. In terms of efficiency, these catalysts are not inferior to platinum-palladium.
Production of permanent magnets
Some intermetallides of lanthanides, for example, YCo5, SmCo5 are magnetic materials with a high value of the product of the induction value by the maximum magnetic field strength: for YCo5 – 9550 T × A/m (1.2 mlngs×E); for SmCo5 – 40290 T ×A/m (5.1mlngs×E). This property makes these materials indispensable for the production of permanent magnets, which are used in the entire spectrum of audio and video equipment production. Magnets for rocket and space technology, neodymium-ferroboron magnets are produced on the basis of neodymium and samarium, they are used in motors and generators of special power.
Production of metal - rare earth garnets
Metal – rare earth garnets 3Ln2O3×5Fe2O3 are finding their application in increasingly wide areas. Thus, iron-yttrium garnets, having ferrimagnetic properties, can simultaneously be both semiconductors and dielectrics, which allows them to be used in high-frequency technology, microwave transmitters and other electronic devices. In recent years, gallium-gadolinium and gallium-scandium-gadolinium garnets have been used as an active medium in quantum paramagnetic amplifiers and high-power solid-state lasers.
In addition, they are used in tunable bandpass filters on magnetostatic waves and are especially widely used in magneto-optics and microelectronic technology as substrates for magnetic garnet films in storage devices based on movable cylindrical domains.
Laser technology
Rare earth elements are used in various classes of lasers (solid, liquid), either as the basis of laser materials, or as an activating additive. Optical quantum generators are known in which solutions of REE chelates are used. Cerium fluorides, lanthanum, yttrium, gadolinium, and cerium oxides are possible as the basis of lasers. Lasers based on Y-Al, Y-Gd garnets doped with neodymium have been developed.
Electro-vacuum, X-ray and radio engineering
In the electro-vacuum industry, REE is used as getters.
Neodymium oxide in electronic devices plays the role of a dielectric with a small coefficient of linear expansion.
The isotope tullium 170 has found an important application for the manufacture of portable generators of soft X-ray radiation for medical purposes and for flaw detection. These generators can replace bulky stationary installations. The promethium isotope 147Pm (T1/2 = 2.7 years) is used for the manufacture of atomic microbeads in which soft b-radiation is converted into electricity.
Agriculture
REE fluorides (CEF3) are used for the manufacture of carbon electrodes to increase the intensity of the glow.
Hydrides - hydrogen accumulators
REE hydrides or their intermetallides are promising as hydrogen accumulators. They are capable of absorbing more hydrogen per unit mass than individual REE oxides. They are cheaper and the materials created on their basis can work in different temperature ranges.
The total consumption of REE in 2010 amounted to 125 thousand tons. When viewed by region, permanent magnets have the highest consumption, accounting for about 27% of total demand in 2010, compared with only 13% in 2000. It is also by far the most valuable sector, accounting for about 47% of the total gross value in 2010. The high growth rates over the past 20 years have been driven by an increase in demand for hard drives, personal audio equipment and small electric motors in some cars. Part of the projected growth of the magnet market until 2015 will come from the use of permanent magnet engines in wind turbines and hybrid electric vehicles (HEV).
Electronics and electrical engineering
The development of the flat-screen display market has a negative impact on the use of cerium oxide as an additive to glass and polishing powders. Nevertheless, the growing demand for flat screens in smartphones and tablets partially compensated for the decrease in the specific consumption of polishing powder per screen. The effectiveness of the polishing slurry has been improved, and recycling is used where appropriate, with concomitant reduction in cerium oxide consumption.
Phosphors and pigments account for slightly more than 6% of the total consumption of rare earth elements, but almost 15% of the cost. Phosphors are the main market for europium and terbium, high-value heavy rare earth elements (HREE), as well as yttrium. The main driver of growth in 2015 was the proliferation of legislation to phase out incandescent bulbs, as a result of which they will be replaced by compact fluorescent bulbs that use rare earth elements.
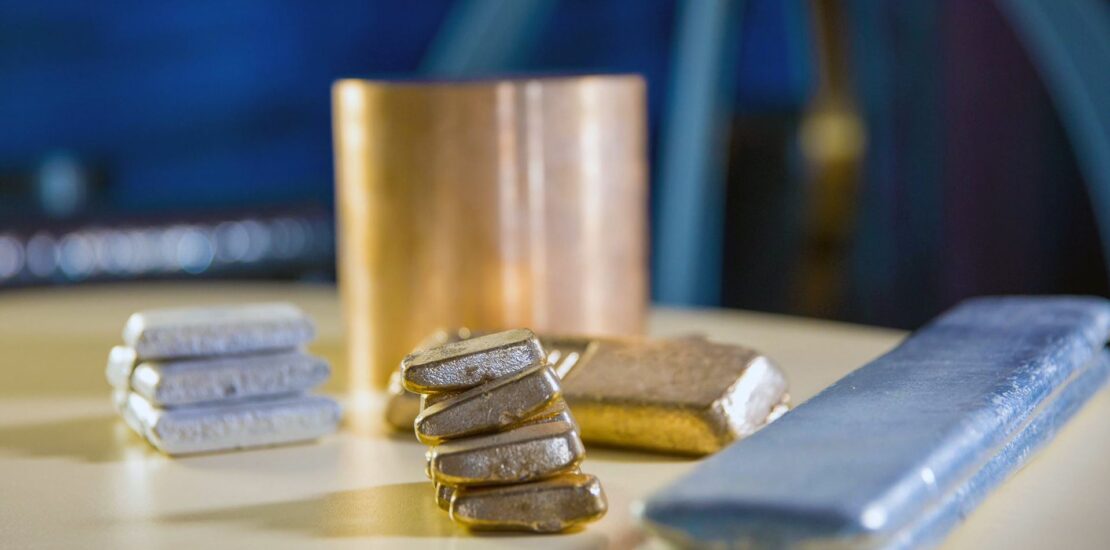
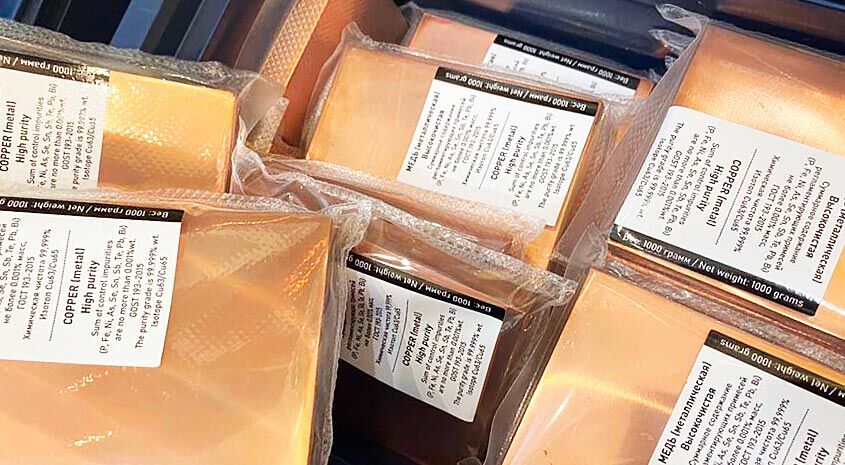
Our products are high purity metals always in stock