Erbium (Er) 68
Chemical element symbol is (Er) and atomic number 68.
Erbium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Heavy Rare Earth Elements (REE).
Carl Gustaf Mosander separated in 1843 discovered erbium. Yttrium mineral gadolinite is used into three fractions, which he called yttrium oxide, Erbium, and terbia. He named the new element after the village of Ytterby where there are high concentrations of yttrium oxide and Erbium .It was not until 1905 Georges Urbain and Charles James developed oxide in pure form. The metal was extracted in pure form in 1934. The natural Erbium consists of a mixture of six stable isotopes.
Characteristics
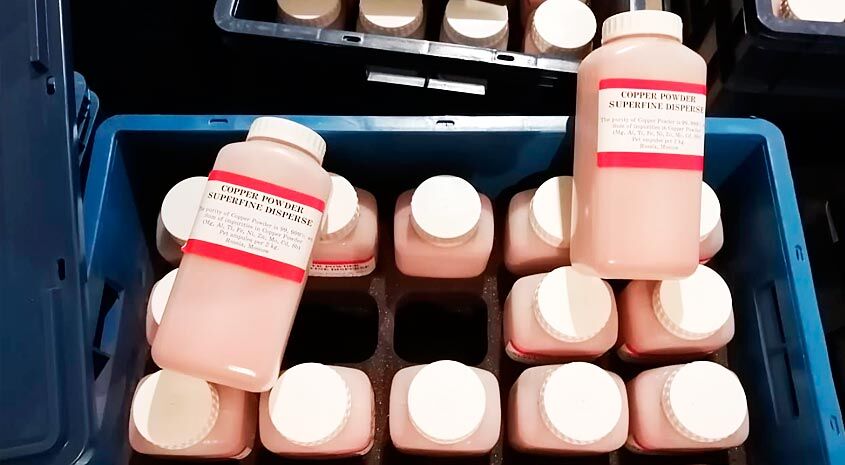
Like most other lanthanides, it is silver grey colour, malleable and ductile at room temperature. Erbium oxides in dry air.
Properties & Applications
The Erbium pure metal is malleable, flexible but stable in air and does not oxidize as quickly as some other Rare Earth metals. Its salts are pink, and the element and bands of sharp features absorption spectra in visible light, ultraviolet, and near infrared. Its sesquioxide is called Erbium oxide. Erbium’s properties are to a degree dictated by the type and amount of impurities present.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
Most indium is used to make indium tin oxide (ITO), which is an important part of touch screens, flatscreen TVs and solar panels. This is because it conducts electricity, bonds strongly to glass and is transparent.
Application field
- Medical: Surgical lasers
- Nuclear medicine: isotope synovectomy fingers in rheumatoid arthritis (Erbium 169)
- Nuclear industry: because of its strong ability to absorb neutrons
- Dentistry: The Erbium laser is the most versatile of dental lasers
- Colours: Glass and porcelain glazes. The Erbium oxide gives a pink colour
Our products are high purity metals always in stock