Europium (Eu) 63
Chemical element symbol is (Eu) and atomic number 63.
Europium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Light Rare Earth Elements (LREE).
Paul Emile Lecog de Boisbaudran rubs his eyes in amazement in 1890, when he looks at the spectral line of a concentrated samarium and gadolinium closer. He was looking at something unknown, that nobody had seen before him. Six years later, Eugene-Anatole Demarcay demonstrated the existence of a new element spectroscopy and first isolated in 1901. The Europium was born. Demarcay companion Marie Curie, then discovered an element that remains one of the most interesting and rare earth that is, with americium, only to be designated by the name of a continent.
Characteristics
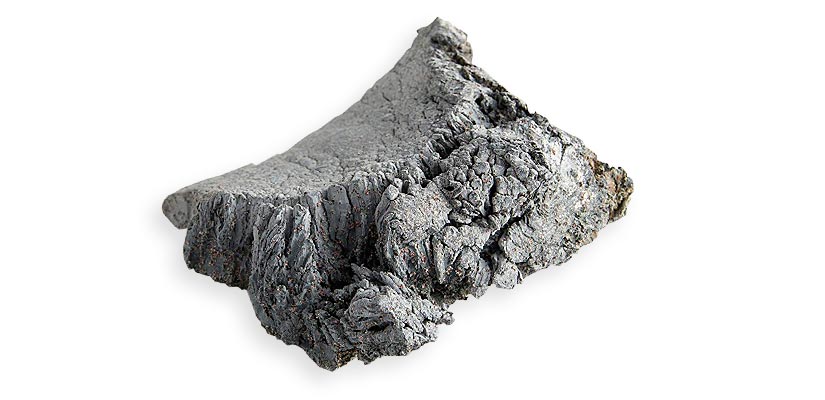
The Europium is the lightest of all heavy metals. It auto-ignite and burns causing a bright red flame. As cerium, Europium exists in two different forms of oxidation, which gives it more flexibility than most other Rare Earths.
Properties & Applications
Because of its important role in the production of LED, LCD and lighting devices, Europium is one of the most rare earth phosphors. As cerium, Europium exists in two different forms of oxidation, which gives it more flexibility than most other Rare Earths.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
Resource Allocation
Relative Supply Risk: 9.5
Reserve Distribution: 50%
Application field
- For Superconductors
- Nuclear fission
- Laser Technologies
- Televisions
- Ceramics protection against radiation in reactors
- Part of the red fluorescent lamps (pleasant spectrum)
Our products are high purity metals always in stock