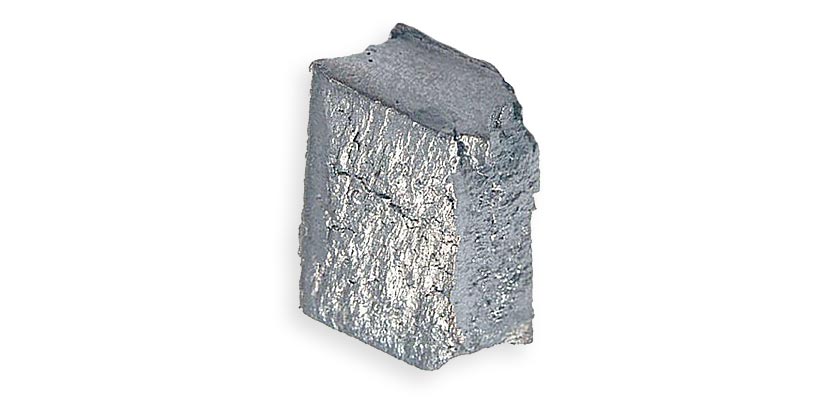
Gadolinium (Gd) 64
Chemical element symbol is (Gd) and atomic number 64.
Gadolinium (Gd) Gadolinium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Heavy Rare Earth Elements (HREE).
Gadolinium oxide was isolated in 1880 by Jean Charles de Marignac Galissard and Paul-Emile Lecog de Boisbaudran prepared the pure metal in 1886. It is named after the Finnish chemist Johan Gadolin, who also discovered and named the mineral, which it is extracted, gadolinite.
Characteristics
Gadolinium is silver grey, malleable and ductile at room temperature. It crystallizes in hexagonal form at room temperature, but when heated to temperatures above 1235 °C, it turns into its form B, which has a body centred cubic structure.
Properties & Applications
Gadolinium has some toxicity. Therefore the Gadolinium compounds are used in medicine as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Gadolinium nanotubes, nicknamed “gado-nanotubes” once injected, Gadolinium based contrast agents, accumulates in abnormal tissues of the brain and body. This accumulation provides a greater contrast between normal and abnormal tissue, which allows physicians to better locate the outgrowth of tumors and rare cells.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
Resource Allocation
Relative Supply Risk: 9.5
Reserve Distribution: 50%
The abundance in the earth’s crust is about 6.2 mg/kg. The main mining areas are China, the US, Brazil, Sri Lanka, India and Australia with reserves expected to exceed one million tonnes. The world of pure Gadolinium production is approximately 400 tons per year.
Application field
- Contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- X-ray systems
- Neutron radiography
- Production of green phosphors for colour television tubes “Protection of nuclear reactors”
- As an electrolyte in fuel cell solid oxide
- Gadolinium is also used in nuclear marine propulsion systems
Our products are high purity metals always in stock