Gallium (Ga) 31
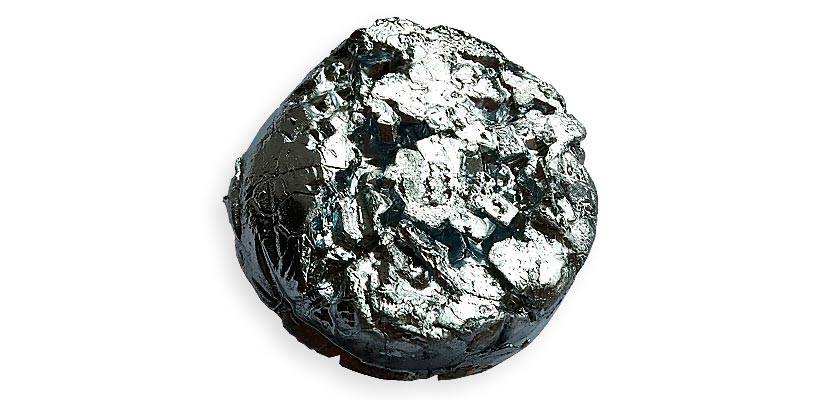
Chemical element symbol is (Ga) and atomic number 31.
Gallium is classified in the group of Intermediate Rare Earth Elements (ETRI).
We are in 1875, in the small town called Cognac, in the South West of France, about 120 kilometers from Bordeaux which is considered a major center for alcohol production. Great wines are produced there and a popular brandy made from white wine is named after the city.
Characteristics
This element critical metal has interesting properties. It melts and shrinks to 29.8 degrees. Today, mixed with indium and tin, it becomes an alloy called Galinstan, which is often used in thermometers since the ban of mercury.
Properties & Applications
The manufacture of semiconductors is nowadays the main use of Gallium. Its use in the semiconductor increases its functionality considerably in comparison with older technologies such as silicon-based semiconductor.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Germany
3. Kazakhstan
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. Germany
3. Kazakhstan
Gross Gallium is also found in many industrial components and High Tech, including LEDs (light emitting diodes). Gallium is a very rare mineral among critic’s metals. 100 tons are produced annually, mainly in China where the majority of the production of Rare Earths and critical metals. It is mainly found in aluminium, zinc and germanium ores.
Application field
- Mostly used for the manufacture of semiconductors
- Used for doping germanium in the production of semiconductors
- Compounds of gallium or indium with arsenic, phosphorus and antimony in the form of solid solutions became the basis for the creation of optoelectronics, expanded the capabilities of microwave technology and microelectronics. They are in demand in semiconductor devices operating at elevated temperatures. GaAs (gallium arsenide) as a semiconductor material is second in popularity only to silicon. At the same time, devices with gallium arsenide work faster and are able to withstand higher temperatures than similar devices on silicon
- Metal compounds are used for the production of LEDs, photodetectors, lasers, solar panels, integrated circuits
- In and Ga alloys with low melting point are used in high-temperature thermometers and pressure gauges, in thermoregulators, fire alarm systems, thermal limiters; instead of mercury in hydraulic valves, rectifiers and current interrupters. For example, an alloy of indium, gallium and tin (galistan) is widely used in thermometers and similar devices where high measurement accuracy is required, but mercury cannot be used
- Metal and its alloys are in demand as a liquid coolant for nuclear reactors
- Metallic Ga is used in neutrino microscopes designed to interact with neutrinos and to create a controlled fusion facility
- Soldered seams made of gallium alloys are resistant to temperatures up to +900 °C, withstand high mechanical loads
- Chloride, nitrate and some other gallium compounds are used in organ synthesis as catalysts
Our products are high purity metals always in stock