Germanium (Ge) 32
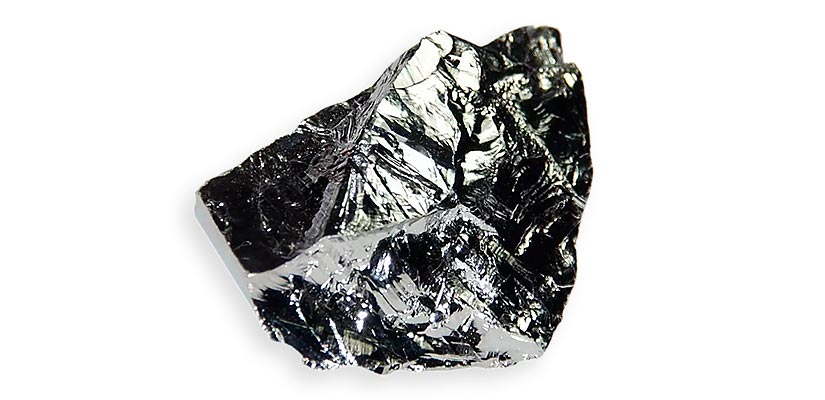
Chemical element Germanium symbol is (Ge) and atomic number 32.
Germanium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Intermediate Rare Earth Elements (ETRI).
The German scientist Clemens Winkler discovered Germanium February 6 1886. Winkler has isolated and identified from the mineral argyrodite from the Himmelsfurst silver mine near Freiberg (Saxony). In 1871, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence (he called this unknown element “ékasilicium Es”) and some of its properties based on its position in the periodic table. Winkler named the new element of the name of his country, by analogy with the name of Gallium (Gaul derivative) chosen by the French scientist Paul-Emile Lecog de Boisbaudran.
Characteristics
Under standard conditions, Germanium is brittle silver-white, semi-metallic element.
Properties & Applications
The pure Germanium oxide is reduced by reaction with hydrogen in order to obtain the Germanium suitable for infra-red optical or semiconductor industry. The main uses of Germanium in 2007 were estimated at 35% for fiber optic systems, 30% for infrared optics, 15% for polymerization catalysts and 15% for electronic and solar electric applications.
The remaining 5% went to other uses such as phosphorus, metallurgy and chemotherapy.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Germany
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. USA
2. Russia
3. China
Resource Allocation
Relative Supply Risk: 8,1
Reserve Distribution:<50%
About 118 tons of Germanium was produced in 2011 worldwide, mainly in China, Russia and the United States. The figures for reserves in the world are not available, but the United States, they are estimated at 450 tonnes.
Application field
- Fiber optic systems
- Used as a night vision system in cars
- Used as a passive thermal imaging for detecting hot in
the military field
Our products are high purity metals always in stock