Lutetium (Lu) 71
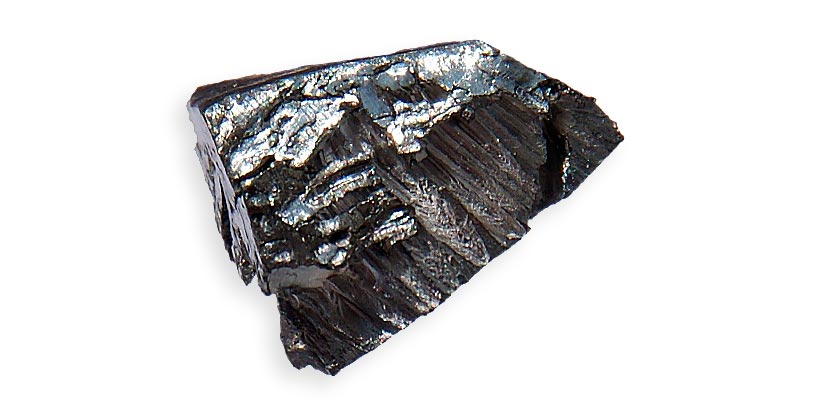
Chemical element symbol is (Lu) and atomic number 71.
Lutetium is a Rare Earth metal classified in the group of Heavy Rare Earth Elements (REE).
Jean Charles de Marignac Galissard first confused the Lutetium with Ytterbium in 1878. French scientist Georges Urbain, Austrian mineralogist Baron Carl Auer von Welsbach and the American chemist Charles James discovered lutetium, derived from the Latin Lutetia independently in 1907. Scientists have proposed different names for the elements: Urban chose neoytterbium and lutetium, while Welsbach selected Aldebaranium and Cassiopeium. These two articles were accusing each other for the publication of the results on the basis of the other party.
Characteristics
The Ytterbium is a shiny silver metal that is relatively stable in air and reacts slowly in water. Like other lanthanides, it is silver grey malleable and ductile at ambient temperature. It must be kept away from the air, especially moist.
Properties & Applications
Because of its rarity and its high price, lutetium has very few commercial uses. However, stable lutetium may be used as catalysts in petroleum cracking in refineries and can also be used in applications alkylation, hydrogenation and polymerization.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
The abundance of lutetium in the crust is only about 0.5 mg / kg. The main mining areas are China, the US, Brazil, India, Sri Lanka and Australia. World production of lutetium is around 10 tonnes per year.
Application field
- Used as phosphorus in LED bulbs
- Ideal for phosphors X ray
- Used in magnetic bubble memory devices
- Catalysts in petroleum cracking in refineries
- Used in magnetic bubble memory devices
Our products are high purity metals always in stock