Praseodymium (Pr) 59
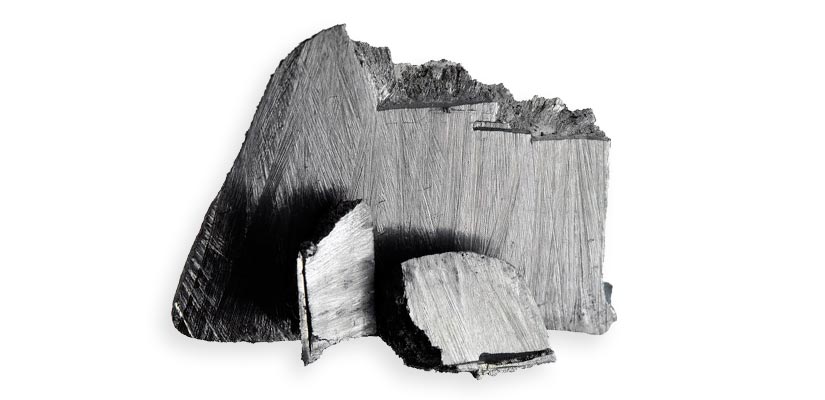
Chemical element symbol is (Pr) and atomic number 59.
Praseodymium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Light Rare Earth Elements (LREE).
In 1841, Carl Gustaf Mosander separates Didymium Rare Earth Lanthanum oxide. In 1874, Per Teodor Cleve discovered that the Dydimium actually consists of two elements. In 1879, Lecoq de Boisbaudran isolates of Samarium Didymium samarskite extracted from ore. In 1885, the Austrian chemist, Baron Carl Von Welsbach Auer, separates into two elements Didymium Praseodynium and Neodymium, which produce different colours salts.
Characteristics
The Praseodynium is a soft metal, silvery, malleable and ductile of the lanthanide group. tis somewhat more resistant to corrosion in air as europium, lanthanum, cerium and neodymium but produces a green slightly adherent oxide layer, which bursts when exposed to air. The metal is thus again exposed to oxidation.
Properties & Applications
Praseodynium is generally used as an alloying agent with magnesium to high strength metal applications in aircraft engines. Itis also used in super magnets, catalytic converters, eye protection against ultraviolet, carbon lighting applications and tomography (CAT scan).
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
Resource Allocation
Relative Supply Risk: 9.5
Reserve Distribution: 97%
World reserves REE were estimated at 110 million tons at the end of 2010, 50% owned by China to the Commonwealth of Independent States CIS intergovernmental entity of 9 of the 15 former USSR (17%), USA (12%), India (2.8%).
Application field
- Laser technology: Praseodymium ions are used to create laser radiation in the infrared range at a wavelength of 105 microns. Praseodymium fluoride is used as a material for the laser itself
- Thermocouple alloys: Praseodymium monotelluride is used to regulate the properties of some REM-based alloys, which are used to create thermocouples. Adjustment of EMF, electrical resistance, increase of mechanical strength of these alloys, cannot do without the use of this praseodymium compound
- Glass production: Praseodymium oxide is used to give the glass, during its manufacture, a pale green shade
- Metallurgy: Praseodymium, as a component of mishmetall, is used for alloying steels. Cobalt and nickel alloys alloyed with praseodymium are added to the composition of magnesium alloys
- Superconductors: The addition of praseodymium to germanium-silicon alloys gives superconductors made on their basis high electrical properties
- Magnetic materials: Praseodymium is used in the manufacture of magnetic cores, which gives them unique properties
- Electrical Engineering: Praseodymium increases the efficiency of using cathodes of electro-vacuum devices. Praseodymium is used in the manufacture of electronic ceramics
- Nuclear engineering: Praseodymium salts are used as a shifting reagent in nuclear magnetic resonance
- Optics: Praseodymium, in the form of oxides, is used in the composition of powders for polishing glass
- Chemistry: Praseodymium is used as a pigment in some chemical compounds
- Space and aviation: Praseodymium is part of the structural materials for the creation of satellites, spacecraft and for aircraft construction
Our products are high purity metals always in stock