Samarium (Sm) 62
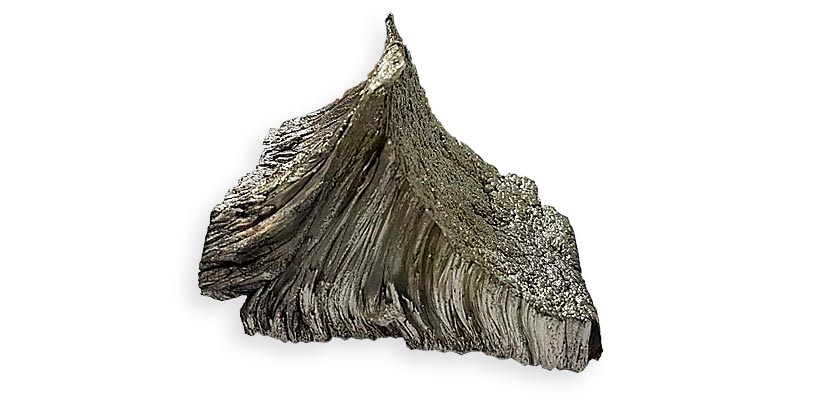
Chemical element symbol is (Sm) and atomic number 62.
Samarium is a Rare Earth Metal classified in the group of Light Rare Earth Elements (LREE).
Samarium was discovered spectroscopically in 1853 by the Swiss chemist Jean Charles de Marignac Galissard, by observing its fine absorption lines in the Didymium. He was isolated (as a mixture of two oxides) in Paris in 1879 by French chemist Paul Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran from Samarskite- (Y) (en), mineral with the chemical formula ((Y, Ce, U, Fe) 3 (Nb, Ta, Ti) 5076). In 1901, the French chemist Eugéne-Anatole Demarcay succeeds in separating the two oxides and discover and europium.
Characteristics
Samarium is a rare metal on Earth. Its silver in colour, relatively stable in air and ignites at 150°C. Three changes in the structure of the metal in particular exist to 734°C and 922°C.
Properties & Applications
The element has no other current application as luminescent compounds because of its radioactivity. Its use as a source of heat and thus electricity in space applications is currently under study and its use as a potential source for portable X-rays.
Supply
Top 3 Producers
1. China
2. Russia
3. Malaysia
Top 3 Reserve Holders
1. China
2. CIS countries (incl. Russia)
3. USA
Resource Allocation
Relative Supply Risk: 9.5
Reserve Distribution: 97%
Application areas are still very limited. Samarium oxide is used in the glass industry, where it is used to filter the infrared light spectrum of the optical lenses.
Application field
- Powerful magnets
- Optical glasses
- Permanent magnets
- Turbo machinery
- Cryogenic uses
Our products are high purity metals always in stock